Chapter 3 Connecting loggers to computers
There are several options with different advantages and disadvantages to connect microcontrollers and dataloggers to computers. Some of the same protocols can also be used to communicate between computers e.g. to upload data to a centralized server.
3.1 Serial port
Serial protocol is the simplest way to communicate between computers and hardware. Physical serial ports have been removed from new computers, but the protocol is still used by numerous devices with USB-adapters.
- Has drivers for any operating system and can be programmed wit almost any programming language.
- Most microcontrollers have a serial port.
- The user needs to set the baudrate (=speed) and sometimes other communication protocols. Maximum speed 115.2 kbits/s.
- Only two devices can be communicate using the same port.
- Several devices interface with microcontrollers with serial port e.g. GPS, LCDs, GSM and GPRS.
Serial ports were originally physical ports in the computer, but
hardware serial ports are now longer used in similar form because they
have been replaced by USB-ports.
However the communication protocol is
so simple and convenient to program that e.g microcontrollers use the
same protocol and USB-adapters are used on the computer to from a serial
port.
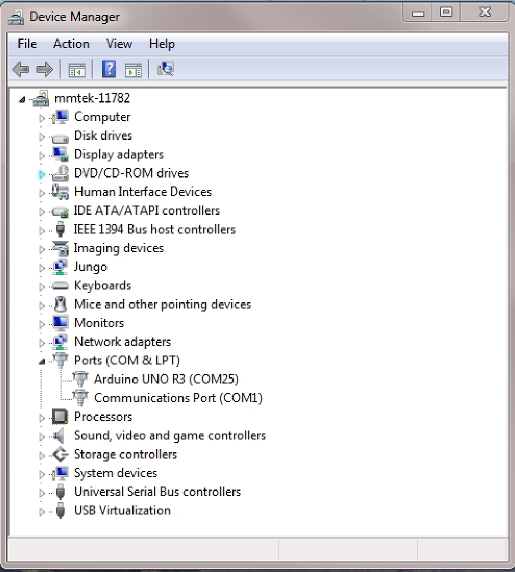
You can find the serial ports connected to your computer from
“Device manager”(You can type
devmgmt.msc
) in windows run dialog (press win+R) to open Device Manager.
The easiest way to see traffic from a serial port is to use a terminal program such as free Bray’s Terminal 1
There are different voltage levels that the serial port protocol can use: microcontrollers typically use TTL level (3.3V or 5V) and computers use 15V, therefore you need to use correct adapter for each device. The communication protocol with different voltage levels is the same so you can use a level shifter circuit to if you need to connect two devices using a different voltage level.
Some instruments still use the +15V serial ports (e.g. Agilent 34970A panel meter that is used in the exercises.) The advantage of the higher voltage level is that it can be used with longer cables.
Serial ports have several different settings for baudrate and other traffic options. Also the wiring may differ between devices. So if you experience problems always check the traffic settings and make sure you use the correct cable. Open the cable to check if you can or make a new one, if you can’t open a cable without breaking it you can use a multimeter to check which wires are connected.
3.2 USB (universal serial bus)
USB-port has become the most popular connection for dedicated DAQ boards. USB has generic drivers for keyboards, mice, printers etc. which makes it possible for devices from diffent vendors to work without separate drivers.
unfortunately there is no device class in the USB standard for for DAQ cards. Therefore you Vendor specific drivers, that need to be programmed separately for each manufacturer and you may not have drivers for all operating systems.
- Programming USB devices is usually more complex than serial port devices.
- Generally used USB 2.0 is quite fast: data transmission at 480Mbit/s
- Newer USB 3.0 standard is specified up to 5 bBit/s, however it is not yet widely used in data acquisition hardware.
- USB port can be used to power devices: 5V, 500 mA.
- Only one device can be connected per port, but 127/controller are allowed using a hub.
3.3 Ethernet
Can be connected directly directly to computer or local network, or to Internet.
- Speed 10, 100 or 1000 Mbit/s.
- Devices get an IP address and multiple devices can be connected via internet or a local network.
- Traffic using TCP/IP or UDP traffic.
- Fairly simple to program. Works on any operating system and can be interfaced with microcontrollers.
- Popular in industrial devices.
3.4 Wireless connections
There are several possibilities for wireless connections that vary in speed , power consumption and signal transmission range . It pays off to spend some time choosing the right one for the application.
The range of the radio signal depends on:
- Frequency. Higher frequencies can transfer data faster, but have shorter range.
- Obstacles. Structures attenuate signals considerably.
- Transmission power
- Antennas. Transmitting and receiving antennas.
- Receiver sensitivity and SNR.
License free bands for radio communication in Europe are 433, 868, 2400 and 5700 MHz. You are not allowed to use devices that operate with 900MHz, those are made for USA.
3.4.1 Bluetooth
Fairly short range and speed <1Mbs. Can be programmed as a serial port. Bluetooth low energy is very popular in human fittness trackers etc.
3.4.2 Zigbee
Modules for short and long range. Forms a mesh network where all radios can talk to each other. Speed <1Mbs. Programmed using a serial port.
- Simple and affordable modules with low power consumption.
- Communication using a serial port, point-to-point or point-to-multipoint networks with \( 2^64 \) devices in a network.
- Different frequency channels: 2.4GHz, 915MHz, 868MHz.
- Sends messages from sensor to sensor enabling longer transmission ranges.
3.4.3 Radiomodems
Radiomodems are usually low frecuency serial port repeaters and can have range of up to 10-20km. Speed <1Mbs.
3.4.4 WLAN
Range some hunders of meters. Speed maximum 100-200Mbs. Programmed using TCP/IP or UDP. Any ethernet device can be connected to a WLAN network.
3.4.5 GPRS
Mobile phone networks. Global coverage within mobile phone network. LTE upload speed up to 50Mbit/s, but depends heavily on network quality. Can be used to transmit fairly large amounts of data from local buffer.
3.5 Exercises
- Compare serialport, USB and Ethernet connection. What is the advantage of each type?
- What factors influence the range of a radio link?